Electrochemical atomic force microscopy mode allows for AFM measurements while the electrochemical reaction is taking place. The AFM itself is not part of the electrochemical reaction, it only acts as an observer. In particular the AFM tip is not conducting and on floating potential to ensure it does not interfere with the electrochemical reaction. With a special electrochemical cell changes on the electrode surface can be monitored in an electrolyte solution. Both the reduction reactions at the cathode and the oxidation reactions at the anode can be studied. Knowledge of these reactions is crucial in applications such as corrosion, batteries and photovoltaics. Thus EC-AFM allows in-situ monitoring of the electrode structure during such reactions. As a result, the relation between the electrode structure / morphology and its electrochemical activity can be established.
Electrochemical studies are usually done in fairly aggressive liquid environments. Thus excellent environmental control and protection of AFM electronics is necessary for good imaging results. The Nanosurf Flex-Axiom combined with the EC-AFM sample holder is ideally suited for these measurements. All the AFM electronics is protected and positioned above the liquid. Special corrosion-resistant material is used for the cantilever holders.
Shown below is a study of the nucleation and growth of copper clusters under electrochemical control. Cyclic voltammograms were used to charactize the electrochemical reactions and derive suitable potentials to observe the topographical changes under stable electrochemical conditions.
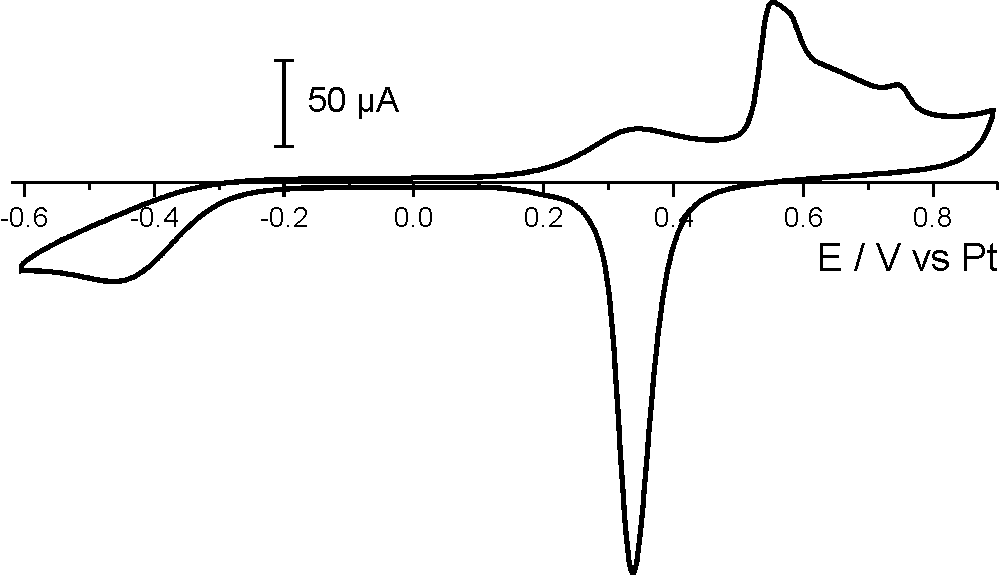
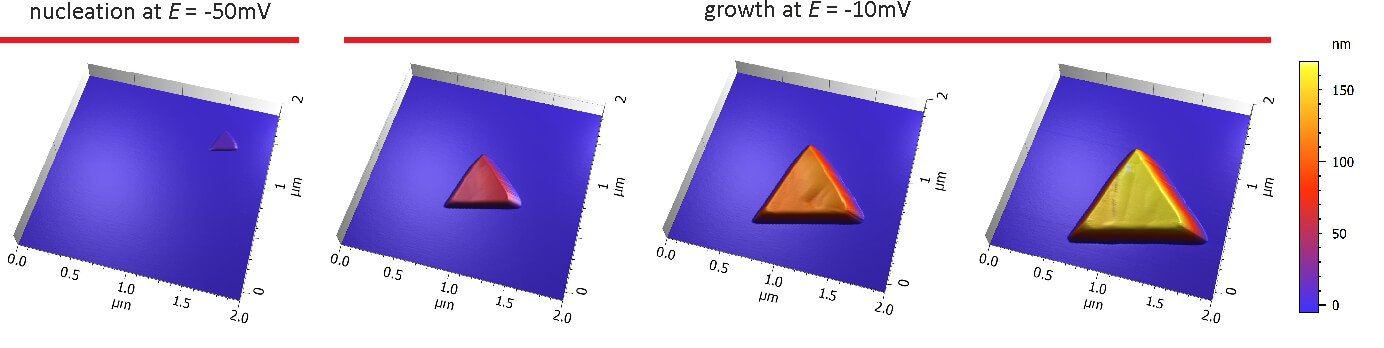
Nucleation was observed by AFM at E = -50mV in sulphoric acid vs. a platinum quasi reference electrode. Increasing the potential to E = -10mV reduced the growth rate and a single copper cluster could be followed by time-lapse AFM. This reaction is reversible and at positive potentials the cluster was dissolved again.
The height of the ECS204 electrochemical stage is designed so that it can also accommodate standard, rod-like electrodes. Further it is equipped with a sealing membrane and gas in- and outlets to allow oxygen free conditions and also means to exchange the electrolyte. In the example below, the dissolution of deposited copper clusters on a polished rod-like platinum electrode at oxidizing conditions was observed by AFM.
Related content
-
Electrochemical AFM with rod-like samples: Cu deposition on a commercial Pt electrode
A unique feature of the Nanosurf Electrochemistry Stage ECS 204 is the capability to handle both flat and rod-like samples for simultaneous AFM and electrochemical measurements. This capability is exemplified here by an in situ electrochemical AFM experiment showing copper electrodeposition and stripping on a commercial rod-like platinum electrode.
-
Poly(vinylferrocene)–reduced graphene oxide as a high power/high capacity cathodic battery material
The preparation and performance of a new cathodic battery material consisting of a composite of poly(vinylferrocene) (PVFc) and reduced graphene oxide (rGO) is described. It shows the highest charge/discharge efficiency (at a rate of 100 A g−1) ever reported for ferrocene–polymer materials.
-
Electrochemical AFM
This report demonstrates the capability of the FlexAFM in studies of charged solid-liquid interfaces. In order to carry out electrochemical(in-situ) AFM experiments, a conductive sample was mounted in an electrochemical liquid cell and connected to a lab-build bipotentiostat. We employed Clavilier-type Au(111) single crystal bead crystal electrodes with facets of micrometer-wide terraces. As ex...
If you have questions, remarks or need more detailed or specific information, just contact us for further assistance.


–reduced graphene oxide as a cathodic battery material .jpg)