Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, Volume 59, Number SI (2020)
Nithi Atthi, Witsaroot Sripumkhai, Pattaraluck Pattamang, Oraphan Thongsook, Rattanawan Meananeatra, Pawasuth Saengdee, Norabadee Ranron, Arckom Srihapat, Jakrapong Supadech, Nipapan Klunngien
Abstract
Researchers from the Thai Microelectronics Center (TMEC) at the National Electronics and Computer Technology Center (NECTEC) and the Department of Materials Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, at Kasetsart University have explored a simple flame treatment method was explored to generate micro-/nanostructures on polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) micro-patterns and published their work in the Japanese Journal of Applied Phyiscs.
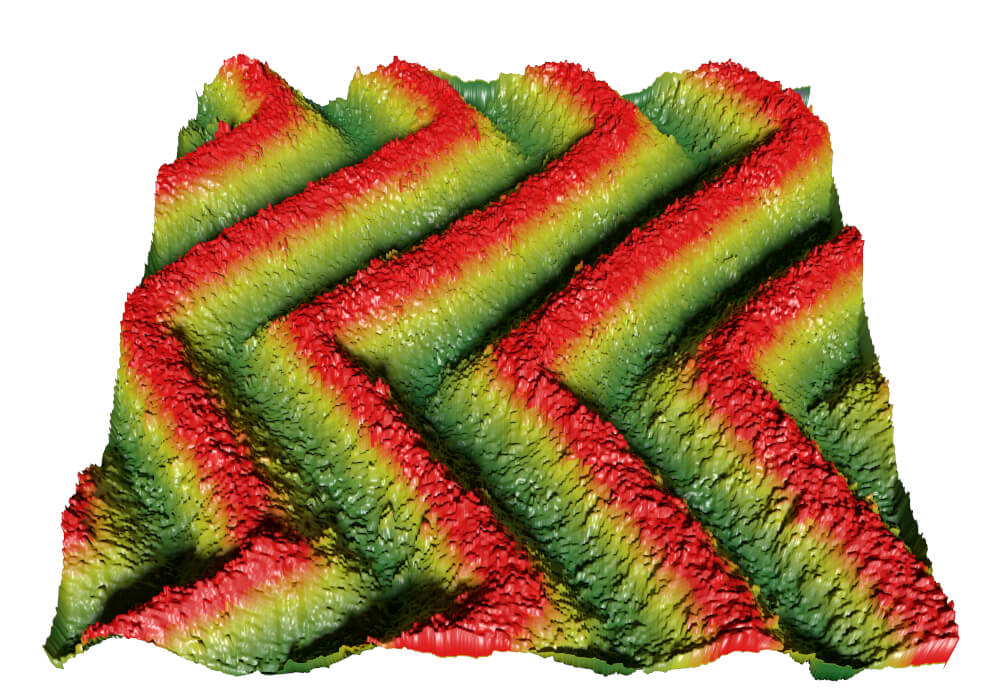
In this research, a simple flame treatment method was explored to generate micro-/nanostructures on polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) micro-patterns. Ethanol soaked paper wipes were used as a flame source at a temperature of 700 ± 20 ºC. After flame-treated for 30 s, a unique flower petal nano-structures were formed on all surface types: flat PDMS (PDMS-FLT) and PDMS with square pillar pattern (PDMS-PIL) and PDMS with rectangular ridge patterns (PDMS-REC).
The average surface roughness (Ra) of the PDMS samples was measured using a Nanosurf CoreAFM.